|
That which does not kill us, makes us stronger - (Friedrich Nietzsche) ...provided we get enough recovery - (Wellness Garage) Chronic stress can play a central role in the development and progression chronic disease and ill health. But stress is not all bad Let’s consider the paradox of stress Protection and damage are the two contrasting sides of physiological processes that defend our bodies against the challenges of daily life, whether or not we call them “stressors.” We respond to stress in two ways:
Our bodies are designed to respond to a challenge (or stress) by
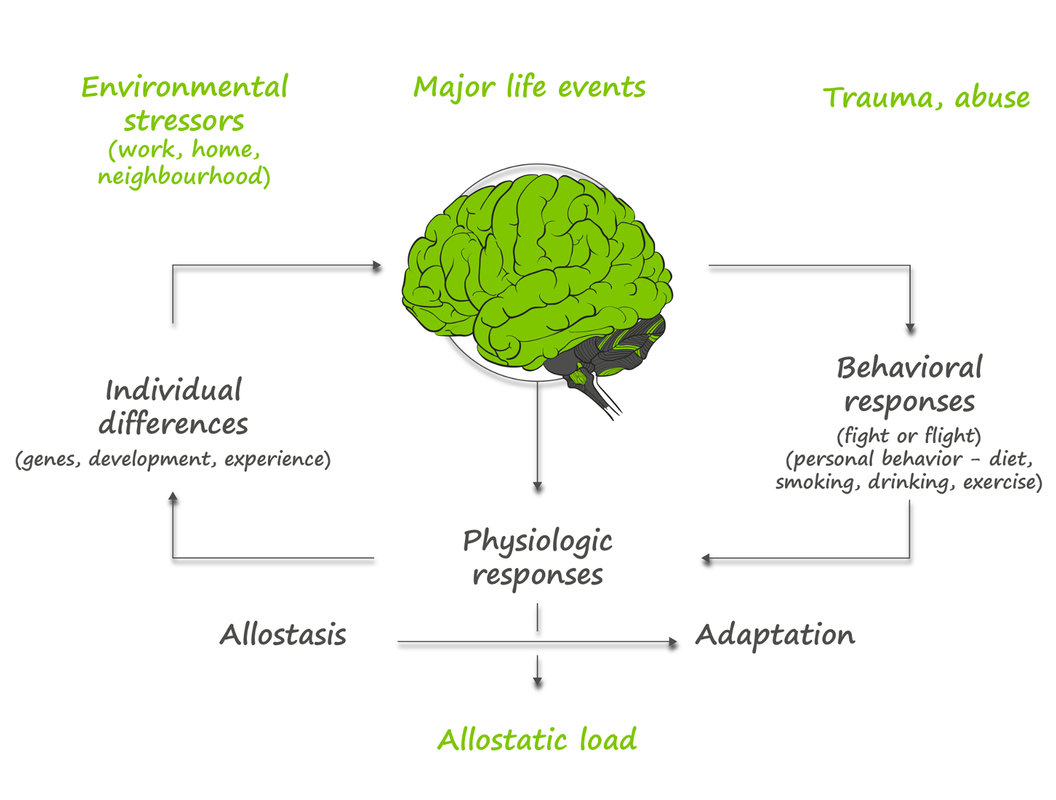
This process is called allostasis – the ability to achieve stability through change. Your response to a stressor is determined by many factors:
ALL of which determine the extent of your physiological response. Over time allostatic load can accumulate OR the individual can adapt. The immediate stress response is mediated by two systems:
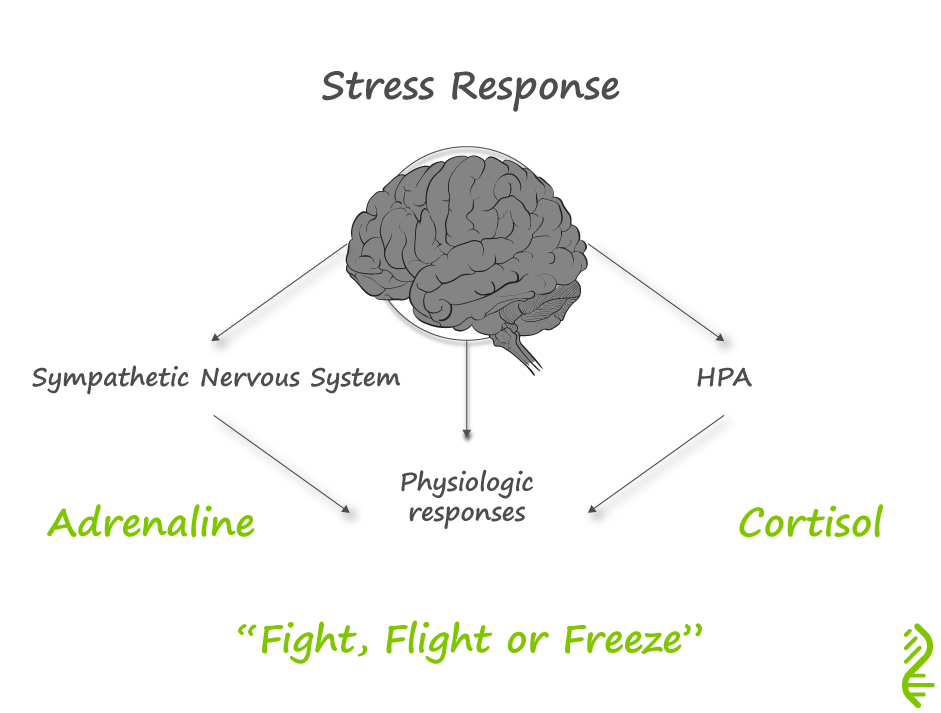
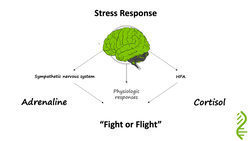 When a situation is perceived as stressful – the hypothalamus sends signals to activate both stress responses. The hypothalamus signals the inner part of the adrenal gland to release adrenaline and which activates the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in:
The effect is immediate and is experienced as the adrenaline rush. The hypothalamus also releases a hormone CRH which activates the pituitary gland to secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) the hormone that stimulates the outer part of the adrenal gland to produce cortisol. Cortisol enables the body to maintain steady supplies of blood sugar for a more prolonged stress. Adequate and steady blood sugar levels help person to cope with prolonged stressor, and helps the body to return to normal. Cortisol does this by:
Once the stress is over the body recovers by:
Every system of the body responds to acute challenge with allostasis leading to adaptation. When these acute responses are overused or inefficiently managed, allostatic overload results. There are 4 patterns to the accumulation of allostatic load:
Remember, three factors largely determine individual responses to potentially stressful situations:
So the key to avoiding the damaging effects of stress is to:
This is why developing stress tolerance is one of our 6 pillars of health Strategies like meditation, yoga, mindfulness, hobbies and anything that brings you into flow can help both the recovery and the perception of stress. Other strategies like ‘stress audits’ can help you identify the areas of life within your control that are causing you stress. Decisions can then be made to alter or avoid these particular situations. Changing your perception of a stressful situation is one of the most powerful ways to develop stress tolerance. Katie Byron has a process called “The Work” in which she walks you through a process that has you answering 4 questions about the situation: Developing a strategy to tolerate stress is a key part of maintaining health - what is your strategy?
|
AuthorDr. Brendan Byrne Categories
All
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
