|
A very compelling read from a New York Times op/ed, making the point that we have made previously on our blog: today's chronic diseases have their origin in the evolutionary mismatch between our current environment and behaviors and what our bodies evolved to be. In this article, we learn how evolution set out to protect us from starvation, infections and injuries leaving us vulnerable to atherosclerosis - the disease process underlying heart disease. https://www.nytimes.com/2019/08/06/opinion/evolution-heart-disease.html?action=click&module=Opinion&pgtype=Homepage At Wellness Garage - we take a precision health approach to atherosclerosis prevention, treatment and reversal, by working with our members through a structured change process: Assess, Change Behaviors, Re-assess and Adjust.
Learn more about what it looks like to do a Precision Health Tune Up and take control of your health. This is the first of a two part series on atherosclerosis and will explain:
What is atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis - commonly known as “ hardening of the arteries” refers to a disease process that causes damage to the arteries resulting in narrowing, blockage, occlusion and even rupture. Atherosclerosis is the underlying cause of most cardiovascular disease (CVD) - including heart disease and stroke.
Atherosclerosis is both very common and very preventable. Our view is that the key to prevention comes from really understanding how atherosclerosis develops. This involves getting past some common misconceptions that have resulted from an oversimplification of the disease through the two dominant conceptual models used to explain atherosclerosis:
The issue with each of these models is that they overlook some key facts and observations:
Before we go further here - let's back up and better understand the disease process:
To summarize, atherosclerosis is caused by an inflammatory response to oxidized lipoproteins within the artery wall. There are three main ingredients that trigger a lesion:
The developing process can be mitigated in its earliest phases by HDL-particles that take away the sub-endothelial cholesterol - even after it is taken up by the foam cells. Evidence shows that the risk of atherosclerosis increases with increasing concentrations of LDL-particles in linear fashion - note this LDL-particle numbers, not LDL-cholesterol concentration. (while LDL-C and LDL-p are generally concordant, ie. they increase and decrease together, this is not always true - especially when insulin resistance is present). LDL-cholesterol is what is commonly reported on the standard lipid panel. A better test to understand your risk is the ApoB100 protein- which gives you the number of LDL-particles as each LDL-particle has one ApoB100 It must be stressed that LDL-P easily enter and exit the sub-endothelial space all the time - it is the oxidation of LDL-P that is key step in initiating atherosclerosis. Only oxidized LDP-P is taken up by macrophages and foam cells. What triggers the oxidation of the LDP-P? Damaged, inflamed or dysfunctional endothelial cells create the conditions for LDL-P oxidation. Common causes of endothelial dysfunction are:
Another key point is that the process that leads to an atherosclerotic lesion is systemic - so just identifying and treating lesions that cause blockage (ie. plumbing model) does not sufficiently decrease risk as there may be other non-obstructive lesions that can rupture and cause acute occlusion. So in essence, with atherosclerosis we have a reinforcing cycle of:
The take-home points to remember are:
At Wellness Garage - we can help you understand and take control of your health. Our comprehensive medical, fitness, nutritional and behavioral assessments give you baseline from which to measure your progress. Our coaching helps you improve your behaviors, one habit at a time. For more information - please book a free consultation. Humans need to eat. Cells throughout the body are predominantly fueled by glucose delivered through the blood. In evolutionary times food was not predictable, most often scarce, sometimes abundant. To maintain a consistent energy supply of blood glucose, evolution created a complex signaling system to control the process, delivering glucose when it is needed and efficiently storing it, when calories are abundant, ready to be mobilized in times of scarcity. Two hormones are central to this signaling process: insulin and glucagon. When blood sugar drops, pancreatic alpha cells release glucagon which then triggers the release of glucose from the liver. Correspondingly, when blood sugars rise, pancreatic beta cells release insulin which promotes glucose uptake in the liver and muscle, storing it as glycogen initially and then when glycogen stores are maximized, insulin prompts the conversion of carbohydrates and proteins to fat, our most efficient way to store calories for the future. Both insulin and glucagon are small proteins recognized by specific receptors on individual cells. This process, developed over 600M years of evolution, now is under challenge in humans. The conditions for which we are optimized: calorie scarcity with intermittent abundance, no longer exist. Instead we live in a world of continuous excess calories, with processed foods that rapidly spike blood sugars and trigger massive insulin release, and correspondingly massive insulin directed storage of excess calories as fat in adipose tissue. For many this process has become a one-way street, the flexibility to shift metabolically from glucose to fat as fuel that was once the key to our survival has, for many people, been lost. They are dependent on maintaining blood sugars through the constant consumption of carbohydrates. - if you find yourself craving sweats, getting tired after eating and feeling generally fatigued - this could be happening to you. As a result of excess calories, sedentary lifestyles and this loss of metabolic flexibility, global levels of obesity are soaring: 2 Billion people are overweight - 650M are obese. In Canada close to 50% of the population is overweight!. With obesity has come a corresponding epidemic of obesity related diseases:
The cellular mechanisms by which insulin resistance manifests are complex and beyond the scope of this blog, but at a high level, dysfunctions in three areas appear to alone, or in combination affect the ability of insulin to efficiently activate the insulin receptor and trigger the cascade of reactions that allows insulin to do it's job:
The process by which insulin resistance progresses to pre-diabetes and diabetes is understandable and predictable - it is also very preventable. As insulin resistance sets in, muscle, fat, and liver cells do not respond properly to insulin and thus cannot easily absorb glucose from the bloodstream. As a result, the body needs higher levels of insulin to help glucose enter cells. The beta cells in the pancreas try to keep up with this increased demand for insulin by producing more. As long as the beta cells are able to produce enough insulin to overcome the insulin resistance, blood glucose levels stay in the normal range. Over time, the processes that led to insulin resistance in the first place cause pancreatic beta cells to become less efficient and eventually triggers beta cell death. As this begins to happen, blood sugars fall out of the normal range and people begin to be diagnosed with pre-diabetes or diabetes on the basis of abnormal blood sugars. The time that it takes to progress from insulin resistance to pre-diabetes is generally in the order of 10-15 years - during this whole time a person will have normal blood sugars and may feel reassured that they do not have diabetes - YET - they are manifesting the underlying process of insulin resistance that will lead to diabetes and it's complications. So the big question that you should be asking is - how do I know whether I have insulin resistance? Direct testing of insulin response is not broadly available, so we are most often left looking for other signs of insulin resistance. For the most part, we can work with this:
My blood sugars are normal, but I think I have insulin resistance, what do I do The good news is the process that leads to diabetes is reversible through lifestyle changes:
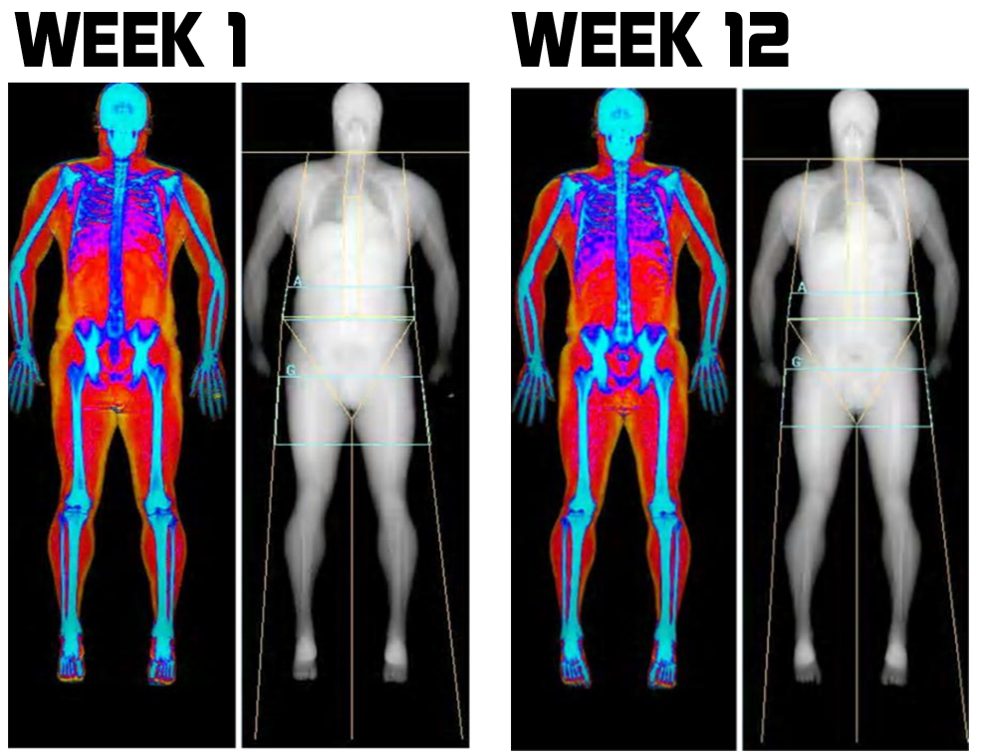
One of the major reasons we started Wellness Garage was to help people intervene early in preventable disease processes like insulin resistance rather than wait until blood sugars become abnormal (after 10-15 years!) and prescribe medications. If you think that you could be affected by insulin resistance - please reach out to us and book a free consultation, we can help you come up with a plan to address your health needs. Dual X-ray Absorptiometry - DXA is the Gold Standard for body composition. The technology uses two x-ray beams of differing energy levels to scan a person’s whole body. The difference in the absorption of the two beams by the three major body compartments: bone mass, lean muscle and fat provides the data that allows for a computer to determine a person’s:
Modern lifestyle, with too much food (of questionable quality) and too little exercise leads to some inevitable consequences. Body fat increases, lean muscle mass decreases and bone density decreases. From a physiological perspective, there is nothing inherently wrong here - this is actually how the body was designed:
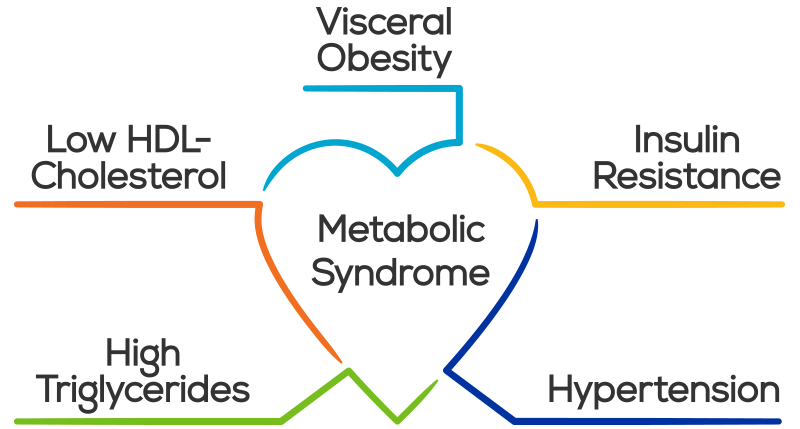
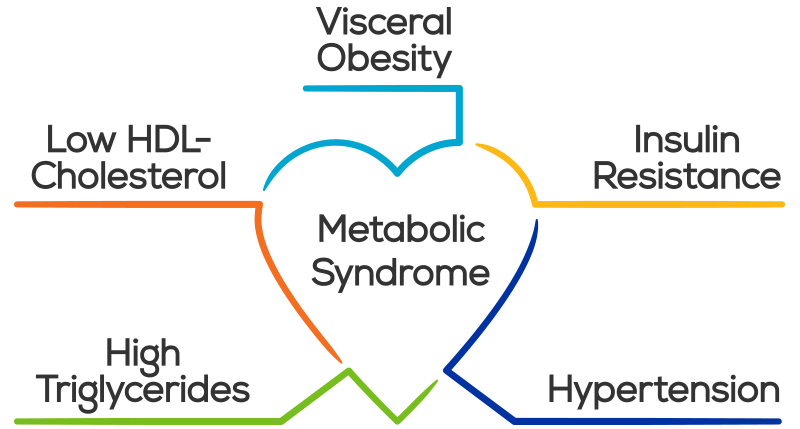
Most often these changes are recognized when a person becomes overweight and we use their Body Mass Index (BMI) - an index that attempts to define the amount of tissue per standardized unit of height - it does this simply by dividing the height by the weight squared and is measured in kg/m2. But BMI does not differentiate between bone, muscle or fat. So if you are very strong with large muscles and large bones on an average or even small frame - your BMI may tell you that you are overweight. Commonly accepted BMI ranges are underweight: under 18.5 kg/m2, normal weight: 18.5 to 25, overweight: 25 to 30, obese: over 30. More challenging then the strong muscular person who is labelled overweight (most physicians generally recognize this), is the opposite situation: a person with decreased lean muscle, decreased bone density and increased fat where their BMI places them as normal even though from a body fat percentage they are obese. This is far harder to detect in clinical practice, and is probably more common than most realize. The second reason to want a DXA - even if, in fact, especially if, you are obese, is to understand the nature of your obesity. Fat accumulation around the visceral organs in the abdomen is highly associated a destructive self reinforcing cycle of inflammation, insulin resistance, high blood sugars, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and in turn more adipose fat accumulation. This viscous cycle, known as metabolic syndrome, is highly associated with diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Shockingly, according to a 2011 study almost 1 in 5 (19.1%) of Canadians are estimated to have metabolic syndrome, and most are undiagnosed, (and I suspect things have gotten worse in the last 7years!) The most common component of metabolic syndrome in Canadians: abdominal obesity. A low tech approach to estimating abdominal obesity is to measure the waist to hip ratio - anything above 0.9 for men and 0.85 for women is considered by the WHO to signify abdominal obesity. Less accurate than a DXA and without the lean muscle and bone density information, but a critical metric nonetheless. Reason #3 - DXA provides hard-to-get-otherwise information
Maintaining lean muscle mass, along with strength and bone density are strongly positive indicators for longevity - or said another way: loss of muscle mass and bone density are associated with premature death. Here the challenge for the clinician is greater than with abdominal obesity. Often there is simply no way to know a patients lean muscle mass and bone density without DXA measurement. Reason #4 - this is the best part So we now know that DXA gives us some really good information, but the best part is that all of the important markers for vital longevity it tracks
Reason #5 - DXA scans are very safe and can be repeated multiple times in a year. But don’t they use x-ray radiation?
Reason #6 - DXA scans are relatively inexpensive DXA for total body composition is not an insured service, so cost will be an issue for some. However, given the nature of the test and the data they produce for many DXA's are a cost effective investment in their health. ($120 for the first test; $100 for follow-up scans.) In summary - 6 Reasons Why DXA Scans are so useful
At Wellness Garage, we are proud to announce that Bodycomp Imaging is locating a DXA scan within our facility that will be available for our clients as part of our assessments. We are very excited to see this technology come to the South Surrey/White Rock area. Clients are free to book with Wellness Garage or Bodycomp at their convenience. * Wellness Garage and Bodycomp are independent businesses - and Wellness Garage derives no profit from DXA scans done at our facility. Today I am going to provide a list of 7 biomarkers for you health - numbers you should know. These are all biomarkers that can be improved through lifestyle interventions - they are numbers that can be normalized and optimized - and in doing so you will reduce your risk for heart disease, diabetes, cancer, Alzeimher's dementia, kidney failure, arthritis and many other conditions. Optimizing these biomarkers will even decrease your risk of premature death. I think this should be a pretty good investment of 15 minutes of reading! (If you want to skip the reading - there is a quick summary at the end of this post).
2. Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT) - optimal < 30 U/L GGT measures a liver enzyme and is commonly described as liver function test most closely associated with the adverse effect of alcohol. GGT is however much more important as it is an indirect measure of the body’s glutathione supply. Glutathione protect cells against the oxidative stress resulting from metabolism. Without this protection the free radicals generated by mitochondria through normal metabolism with oxygen would accumulate, overwhelm and damage the mitochondria and the cell. In normal ageing it has been shown that it is this accumulation of oxidative stress that leads to many of the age-related diseases. In many ways, glutathione is consider the master antioxidant: working with as part of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase to protect membranes from oxidation, enabling Vitamin E and C in their anti-oxidant capacities as well as working directly. Glutathione is also a key component of the Phase II metabolism (detoxification) of drugs, hormones and xenobiotics where it works as a component of an enzyme Glutathione s-transferase (GST) that conjugates heavy metals, toxins and other compounds so that they become water soluble and can be excreted in the bile or urine. Exposure to high levels of toxins that overwhelm glutathione in its Phase II metabolic role will lead to oxidative stress. 3. hsCRP - high sensitivity CRP - optimal < 1.0 Again another topic I have recently blogged about: chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is at the root of 7 of the top 10 causes of death accounting for 80% of all deaths in our society. The most insidious aspect of this type of inflammation is its silent nature that allows for damage to occur without diagnosis. HsCRP is the gold standard for assessing chronic inflammation - optimizing this number through behavioural change - diet, exercise, stress reduction - decreases the risk for many diseases. 4. Blood Pressure - optimal <115/75 (systolic/diastolic pressures measured in mmHB) This is the simplest - something that you can do at home, at the local pharmacy and with your doctor. Normal blood pressure is 120/80. Recently there were major headlines in the US, noting a change in the definition of high blood pressure (hypertension), lowering the definition threshold to 130/80 from 140/90. While this change dramatically increases the number of people who will be diagnosed with hypertension - not all will automatically be recommended medications. Those recommendations will depend on a person’s overall risk for cardiovascular disease - anyone with a 10% or greater risk should aim to bring the BP below 130/80. High blood pressure or hypertension is quantitatively the most important modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease (the largest contributor to premature death in our society). It is also a significant risk factor for both kidney and heart failure. For every 20 mmHg increase in diastolic blood pressure above 75, the risk of death from heart disease or stroke doubles. Elevations in blood pressure are caused by dysfunctions within core biological systems
5. Fasting Blood Glucose and or HbA1c: optimal FBS <5.2mmol/L (normal <5.6 mmol/L); optimal HbA1c <5.0% Maintaining normal blood sugars is one of the most important and tightly regulated functions in your body. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the condition when your body cannot maintain normal blood glucose levels. Type I DM is an autoimmune disease where the pancreas stops producing insulin. Type II DM, is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body no longer responds normally to insulin. In order to maintain blood sugars, the pancreas increases production of insulin - leading to elevated insulin levels which in turn trigger inflammatory changes, which in a vicious cycle further worsens insulin resistance. Insulin resistance precedes Type II Diabetes and can remain undetected for years, as glucose levels are maintain as normal until the pancreas begins to fail, which is relatively late in the process. Diabetes is diagnosed when FBS >7.0 or HbA1c >6.5% Type II DM is currently at epidemic levels globally having tripled since 2000. Almost 500M people or 1 in 11 have diabetes at an estimated cost of $850M. The direct complications from diabetes come from damage to blood vessels at two levels:
6. TG/HDL - Triglyceride/HDL ratio - optimal <1.0 Of all the information that can be derived from a lipid panel the TG/HDL ratio provides the best information about risk. TG/HDL is an excellent marker for insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome When elevated above 3.5 - this is the simplest test to identify atherogenic dyslipidemia, which is marked by the joint occurrence of elevated TG, low HDL and atherogenic, small, dense, LDL particles. This is highly predictive of cardiovascular disease. As we have seen above insulin resistance is the precursor to Type II DM and is often silent and undiagnosed, and is also one of the major causes of chronic inflammation. 7. Android:Gynecoid Fat Ratio - optimal <1.0 The major cause of the global diabetes epidemic is the associated obesity epidemic. Over 2B people are overweight with about 600M reaching the definition of obese (BMI >30). For obese people cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death and disability, followed by diabetes. Kidney failure and cancer are the other major causes of death. Obesity, through adipocyte dysfunction leads to a chronic inflammatory state that predisposes an individual for many diseases. Abdominal or visceral fat contributes disproportionately to this inflammatory response as compared to peripheral fat. The best way to measure visceral fat is with a DXA body scan, which provides you with android:gynecoid fat ratio. The ratio correlates with insulin resistance, showing the clear link between visceral fat and the pathogenesis of diabetes. The added benefit of getting a DXA scan is getting understanding your lean muscle mass and bone density. As you age maintaining lean body mass and bone density are both essential for vital longevity avoiding age-related sarcopenia and osteoporosis. A good alternative (without the extra bone and lean body information) is a waist:hip ratio. The optimal ratio for men in <0.85 and women <0.75. Abdominal obesity is also a marker for metabolic syndrome - a cluster of conditions that carry risk individually but are collectively carry massive risk:
As you can see, all of the risks for metabolic syndrome have been covered by our 7 numbers.
According to a recent study - almost 1 in 5 Canadians, including 40% of people over 65 have metabolic syndrome . Unfortunately, many are unaware of it and have placed themselves at massively increased risk for diabetes, heart disease and premature death. In Summary - 7 Numbers You Should Know
Inflammation is the normal process by which the body responds to injury. When cells are damaged by trauma or infection, they send signals that mobilize the bodies immune system to understand and address the situation. The acute inflammatory response is recognizable by five cardinal signs: calor; rubor, dolor, tumor and functio laesa; if you have just twisted your ankle: it’s warm, red, painful, swollen, and you cannot use it. This response makes sense as it alerts you to your injury, and forces you to rest while facilitating the repair, turnover and adaptation of the injured tissues, or in the case of infection inflammation also prevents the spread of pathogens to nearby tissue. Without inflammation, we would not survive. Our challenge is that inflammation is meant to be an acute, self-limited process that facilitates healing. Chronic inflammation, unlike acute inflammation is a prolonged, maladaptive, low grade, persistent and dysregulated process that is the major contributor to chronic disease and ageing in our society. This silent but destructive nature makes inflammation a special challenge; by the time it is recognized, much of the damage has been done. Inflammation is implicated in 7 of the top 10 causes of death in Western societies accounting for over 80% of deaths. It is chronic inflammation that represents perhaps the biggest threat to our health and through the epidemic of chronic disease affects the sustainability of our health care systems.
So where does chronic inflammation come from?
The large variety of stimuli that fuel inflammation converge on a few basic mechanisms and pathways within cells - specifically the activation of the transcription factors NF-κB and Nlrp3 inflammasome which activate gene transcription and the production of inflammatory molecules called cytokines that interact with other cells to elicit a cascading response. This response leads to increased plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Interleukin-6, IL-6, Interleukin-1, IL-1 and Tumour Necrosis Factor-α, TNF-α) as well as increases in the main inflammatory biomarkers such as C-Reactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid A. This generalized pro-inflammatory state, interacts with genetic and environmental factors to potentially trigger the onset of inflammation-related diseases:
Given the multitude of triggers and profound potential consequences that chronic inflammation has, the logical question (if you have read this far) is: Am I inflamed? The standard test for this in the clinic is the high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) - anything greater than 1.0 nmol/L suggests a low-grade inflammatory process, with levels greater than 3.0 nmol/L associated with elevated risk for heart disease (atherosclerosis). Levels greater than 10 nmol/L suggest an acute inflammatory response (infection). What is an optimal strategy to avoid inflammation? 1. Maintain optimal gut microbiota health and prevent leakage of gut microbes into the body
If you are having symptoms or have concerns about intestinal permeability - there are tests that we can do to determine whether leakage of microbes from your gut is contributing to your inflammation. Finally, if you are really interested you can check your microbiome and assess it's overall health - two caveats here: 1) there is huge variability between tests - these tests are really just snap-shots; and 2) there really is very limited data from these tests to direct you to a more specific response then I have outlined. 2. Minimize cellular damage from oxidative stress
4. Minimize the deleterious effects of high blood sugars and/or high insulin Our society is in the midst of a diabetes epidemic - it is estimated that between 50-70% of the population has been diagnosed with diabetes, elevated blood sugars (pre-diabetes) or elevated insulin levels (insulin resistance - the precursor to diabetes). While there are clear genetic risk factors, the overwhelming evidence points to lifestyle: poor diet - excessive nutrients of poor quality - high carbohydrate, high fat, combined with physical inactivity leads to elevated insulin levels which initially maintain blood sugar levels at the expense of increasing the storage of calories in fat. This increased fat storage leads to obesity with overloaded fat cells becoming dysfunctional and senescent and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines which in turn cause insulin resistance - creating a vicious cycle. The inflammation eventually affects the pancreatic beta cells, decreasing their ability to secrete enough insulin to maintain blood sugars and a person is diagnosed as diabetic. The frightening part of this scenario is that it often takes 10-20 years to go from insulin resistance to diabetes - during that time levels of chronic inflammation increase as do the associated risks. For diabetes and insulin treatment and prevention the place to start is with diet as it is the most likely culprit. A whole food, low carbohydrate, healthy fat approach is the way to go. For diabetics on medication - ketogenic diets have an excellent track record as a therapeutic intervention to decrease or eliminate medications. As you can see from these strategies to avoid inflammation, the answer lies in your behaviours - especially eating, exercising, sleep and stress. Your optimal strategy will come from assessing and understanding your current situation and addressing your behaviours in a systematic fashion. If you are overweight (or simply over 40) you should, at a minimum, know your hsCRP, fasting blood sugar, HbA1c (3 month average of blood sugars), HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides and GGT (liver enzyme that also is a key marker of oxidative stress), as well as your waist to hip ratio. These are tests that every family doctor can (or probably has already) done for you - the important thing is for you to know. If any of these tests are abnormal (or not optimal), you should develop your own strategy to getting well. If these tests are normal, you should still review your core behaviours and assess what can still be improved. At Wellness Garage, we deliver comprehensive lifestyle medicine assessments reviewing all of this data, along with other optional tests that are not routinely offered in the publicly funded system: molecular data (genomics, metabolomics, proteomics, microbiome, and other advanced diagnostic tests), DXA scans (to assess body composition). We use all of this data to help you build the optimal strategy for your own personal wellness. We then can match you to a personal coach to help you implement the behavioural changes necessary. |
AuthorDr. Brendan Byrne Categories
All
|




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
